Imagine this scenario: you’re browsing a website, eagerly searching for information, when suddenly, you’re faced with a frustrating message – “Error 404: Page Not Found.” We’ve all encountered it at some point. This error page, also known as a 404 error page, can be a roadblock in the user’s journey. In this article, we’ll delve into the world of 404 errors, understand their significance, and explore effective ways to fix them.
- Introduction
- What is a 404 Error Page?
- Why is a 404 Error Page Important?
- Common Causes of 404 Errors
- Impact of 404 Errors on SEO
- How to Identify 404 Errors
- Best Practices for Fixing 404 Errors
- Step-by-Step Guide to Fixing a 404 Error
- Implementing a Custom 404 Error Page
- Redirecting 404 Errors
- Monitoring and Resolving 404 Errors
- Tools to Help with 404 Error Management
- Preventing 404 Errors
- Conclusion
Introduction
In today’s digital landscape, where websites play a crucial role in our online experience, encountering a 404 error can be a source of frustration. A 404 error occurs when a user attempts to access a web page that doesn’t exist or has been moved or deleted. It’s important to address these errors promptly as they can negatively impact user experience and even harm your website’s search engine optimization (SEO) efforts.
What is a 404 Error Page?
A 404 error page is the message displayed when a user tries to access a non-existent page. It indicates that the requested page could not be found on the server. Typically, it includes a brief description of the error and may provide suggestions or links to navigate back to the website’s main pages or perform a search. Customizing your 404 error page can make it more user-friendly and help retain visitors who encounter this error.

Why is a 404 Error Page Important?
A well-designed and informative 404 error page serves several purposes. Firstly, it helps maintain a positive user experience by guiding visitors back to relevant content within your website. Secondly, it prevents users from abruptly leaving your site, reducing bounce rates and increasing the chances of retaining them as engaged users. Lastly, a customized 404 error page can also contribute to your overall brand image and demonstrate professionalism.
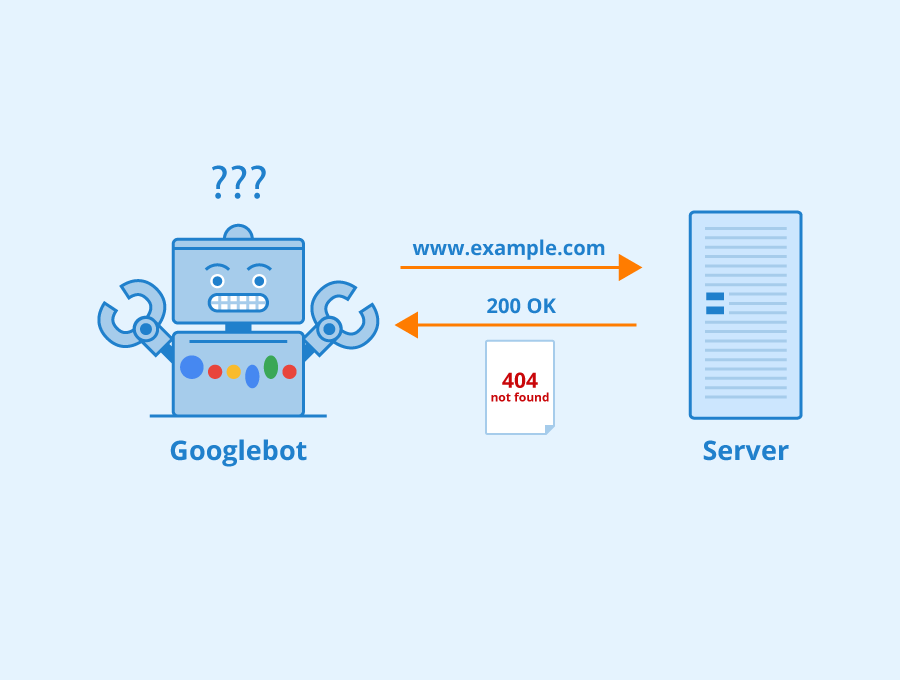
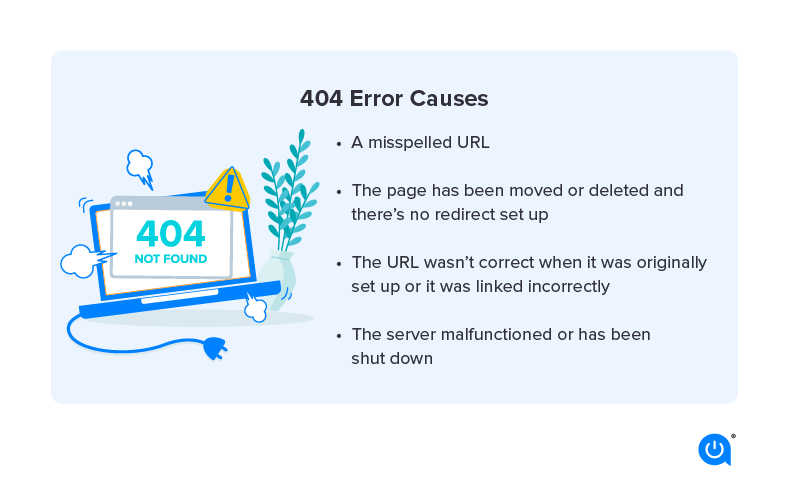
Common Causes of 404 Errors
Several factors can lead to 404 errors on your website. One common cause is when a page is deleted or moved without implementing proper redirection. Other reasons include mistyped URLs, broken links from external websites, and outdated internal links. Additionally, when a website undergoes restructuring or a content management system (CMS) migration, it’s crucial to ensure that all old URLs are redirected correctly to prevent 404 errors.
Impact of 404 Errors on SEO
404 errors can have a significant impact on your website’s SEO. When search engine crawlers encounter multiple 404 errors, they may interpret them as a sign of poor website maintenance, potentially resulting in lower rankings. Moreover, if external websites link to pages that return 404 errors, it can negatively affect your backlink profile and referral traffic. Therefore, addressing and fixing 404 errors is crucial for maintaining a healthy SEO strategy.
How to Identify 404 Errors
To identify 404 errors on your website, you can utilize various tools and techniques. Website analytics platforms often provide reports on 404 errors, indicating the specific URLs that return this error. Additionally, monitoring tools and SEO crawlers can scan your website for broken links and highlight pages that need attention. Regularly checking your website’s error logs can also reveal patterns and help you identify recurring 404 errors.
Best Practices for Fixing 404 Errors
When confronted with 404 errors, it’s essential to handle them promptly and effectively. Here are some best practices to consider:
- Audit Your Website: Conduct a thorough audit to identify pages returning 404 errors and determine the root causes.
- Implement Redirects: For deleted or moved pages, set up appropriate redirects to guide users and search engines to the correct pages.
- Update Internal Links: Review and update internal links across your website to ensure they point to existing pages.
- Fix Broken External Links: If external websites link to pages that no longer exist, reach out to the site owners and request an update or redirect.
- Create Custom 404 Error Pages: Craft informative and user-friendly error pages that provide clear navigation options and encourage users to explore other content on your website.
Step-by-Step Guide to Fixing a 404 Error
Fixing a 404 error involves a systematic approach to ensure the best possible user experience and SEO outcomes. Follow these steps to resolve a 404 error effectively:
- Identify the Error: Understand the specific error message and determine whether it’s a temporary or persistent issue.
- Check for Typos: Verify the URL for any typos or errors, ensuring it matches the intended destination.
- Clear Browser Cache: Clearing the cache can help resolve certain temporary issues that trigger 404 errors.
- Refresh the Page: Sometimes, a simple page refresh can rectify the error if it was caused by a temporary glitch.
- Search for the Page: If you’re unable to find the page, use the website’s search functionality or sitemap to locate the content.
- Contact Website Administrator: If you believe the error is due to website misconfiguration, reach out to the website administrator for assistance.
Implementing a Custom 404 Error Page
Creating a custom 404 error page allows you to turn a potentially frustrating experience into an opportunity to engage and retain users. Consider the following tips when designing your custom error page:
- Clear Message: Provide a concise and friendly message explaining the error and offering guidance.
- Navigation Options: Include prominent links to important sections or popular content on your website.
- Search Bar: Incorporate a search bar to allow users to find the information they were seeking.
- Branding and Design: Maintain consistent branding elements to reinforce your website’s identity.
- Humor or Creativity: Injecting humor or creativity into your error page can help alleviate frustration and leave a positive impression.
Redirecting 404 Errors
Redirecting 404 errors involves guiding users and search engines from the non-existent page to a relevant and functioning page. There are two primary methods for redirecting:
- 301 Redirect: A permanent redirect informs search engines that the requested page has been permanently moved to a new URL. This ensures that users and search engines are directed to the correct page.
- 302 Redirect: A temporary redirect indicates that the requested page is temporarily unavailable but will be back at the original URL. This is useful when performing maintenance or when a page is expected to return shortly.
Monitoring and Resolving 404 Errors
To effectively manage and resolve 404 errors, regular monitoring is crucial. Consider implementing the following practices:
- Periodic Audits: Conduct regular audits to identify and address new instances of 404 errors.
- Monitor External Links: Monitor backlinks pointing to your website and fix any broken links.
- Track Error Reports: Utilize website analytics and monitoring tools to track and analyze 404 error reports.
- Set Up Alerts: Configure notifications or alerts to stay informed about significant 404 errors.
- Collaborate with Web Developers: Work closely with web developers to implement effective solutions and prevent future occurrences.
Tools to Help with 404 Error Management
Several tools can simplify the management of 404 errors and enhance the efficiency of the fixing process. Here are a few noteworthy options:
- Google Search Console: Google Search Console provides a detailed report on crawl errors, including 404 errors, allowing you to identify and resolve them promptly.
- Broken Link Checkers: Various online tools can scan your website for broken links and help you identify pages returning 404 errors.
- Website Monitoring Services: Employing website monitoring services can provide real-time notifications for 404 errors and enable proactive resolution.
- SEO Crawlers: SEO crawling tools like Screaming Frog or SEMrush can scan your website for broken links and provide comprehensive reports.
Preventing 404 Errors
While it’s impossible to completely eliminate 404 errors, you can take proactive measures to minimize their occurrence. Consider the following preventive strategies:
- Regular Content Audits: Conduct routine content audits to identify outdated or redundant pages that can potentially trigger 404 errors.
- Implement Proper Redirection: Whenever you delete or move pages, set up appropriate redirects to ensure a seamless user experience.
- Update Internal Links: Keep internal links up to date, especially when making changes to your website’s structure or content.
- Educate Content Contributors: Provide guidelines and training to content contributors, emphasizing the importance of accurate linking practices.
- Monitor Website Changes: Whenever you make significant changes to your website, closely monitor for any resulting 404 errors and address them promptly.
Conclusion
In conclusion, a 404 error page is an essential aspect of website management and user experience. By understanding the causes of 404 errors, implementing best practices to fix them, and creating a custom error page, you can enhance user satisfaction, reduce bounce rates, and maintain a positive SEO performance. Regular monitoring, redirecting, and preventive measures are key to resolving 404 errors promptly and ensuring a seamless browsing experience for your visitors.




